Big Data deals mainly with two types of data, structured and unstructured. In addition, it is often recognised by the large amount of data it deals with on a day-to-day basis. But it is not the amount of data that is important. What matters with Big Data is what organisations do with the data. Big Data can be analysed for insights that lead to better decisions and strategic business moves.
It is a complex technique as it deals with a large volume of data, complex and interrelated data and very changing data in a very short time, which makes it difficult to understand and work with the data.
Although the size used to determine whether a given dataset is considered Big Data is not firmly defined and continues to change over time, most experts currently refer to a volume of 30 to 50 terabytes.
As we have mentioned, Big Data is complex not only because of the large amount of data but also because of the data itself. It must be taken into account that unstructured data can work with frequencies or responses that could not be analysed before (movements, gestures, temperatures...).
This methodology or area allows companies to analyse data more quickly and accurately. It also allows them to eliminate problem areas before the problems kill their profits or reputation.
Big Data analytics helps organisations leverage their data and use it to identify new opportunities.
The three major benefits of BIG DATA:
Although it is a technical and somewhat complex process, it could be divided into 3 phases to understand what BIG DATA is about or how it behaves:
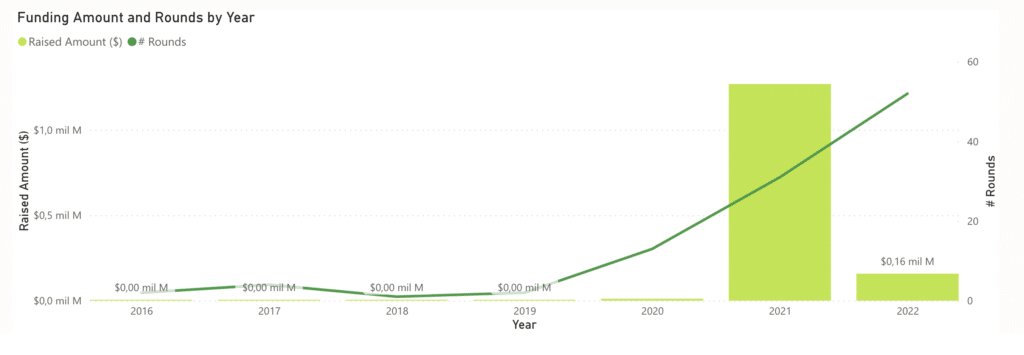
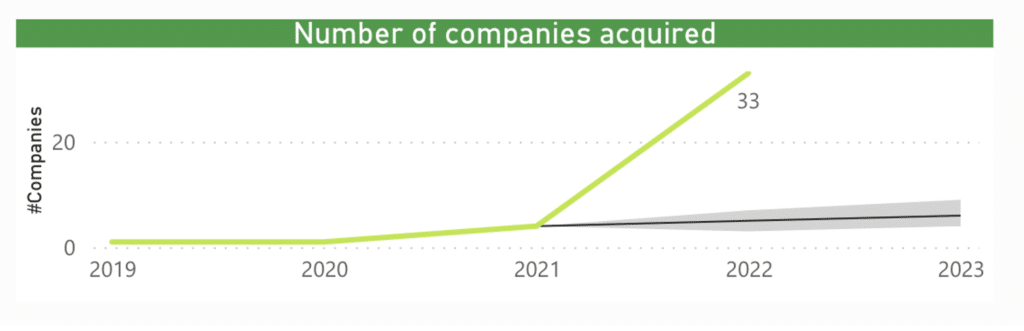
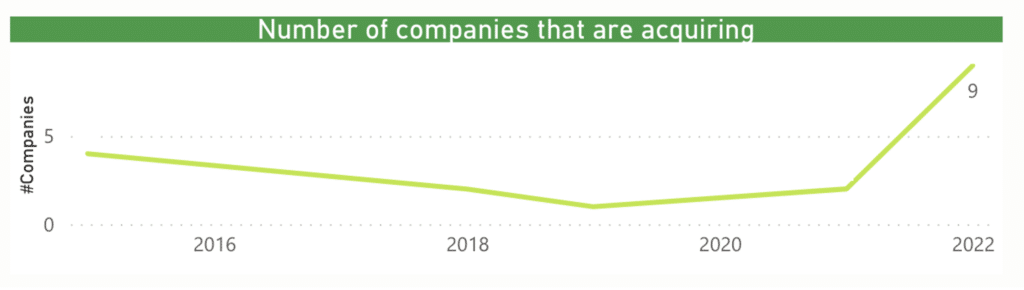
2021 was a very good year for the sector and 2022 seems to be a very good year for the sector, although it still does not reach the same high levels as the previous year. We should bear in mind that 2022 is already at the same levels of M&A transactions in the BIG Data sector in 2022.
INDEX BIG DATA